Having radiotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Radiotherapy is a treatment for some people with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). It uses high energy rays similar to x-rays to destroy cancer cells.
You have radiotherapy treatment in the hospital radiotherapy department. You usually have a course of radiotherapy split into daily treatment sessions. The length of your treatment course depends on the type and  of your NHL.
of your NHL.
When you might have it
Your treatment depends on what type of NHL you have. If you know what type you have, you can read more about your treatment by selecting your type from the menu page.
For low grade NHL
Low grade NHL tends to grow slowly. You might have radiotherapy as your main treatment. You have it to the affected lymph nodes if your NHL is stage 1 or stage 2.
For high grade NHL
High grade NHL tend to grow faster. You might have radiotherapy after treatment with chemoimmunotherapy.
As part of a stem cell transplant
You might have total body irradiation (TBI) as part of a  . TBI means you have radiotherapy to your whole body. This to kill off remaining lymphoma cells.
. TBI means you have radiotherapy to your whole body. This to kill off remaining lymphoma cells.
Palliative radiotherapy
Palliative treatment aims to control symptoms of advanced lymphoma rather than cure it. You sometimes have radiotherapy to control symptoms of advanced NHL.
How often you have radiotherapy
You have radiotherapy treatment in the hospital radiotherapy department.
The full dose of radiotherapy is usually divided into a number of smaller doses called fractions. This allows the healthy cells to recover between treatments. You usually have one fraction a day, from Monday to Friday.
These daily treatments make up a radiotherapy course. The length of your radiotherapy course depends on your situation. It might last a few weeks.
You can also have radiotherapy to help with symptoms or slow down the growth of your lymphoma. This is called palliative radiotherapy. You might just have one dose of palliative radiotherapy although sometimes the course is longer.
The radiotherapy room
Radiotherapy machines are very big and could make you feel nervous when you see them for the first time. The machine might be fixed in one position. Or it might rotate around your body to give treatment from different directions. The machine doesn't touch you at any point.
Before your first treatment, your  will explain what you will see and hear. In some departments, the treatment rooms have docks for you to plug in music players. So you can listen to your own music while you have treatment.
will explain what you will see and hear. In some departments, the treatment rooms have docks for you to plug in music players. So you can listen to your own music while you have treatment.
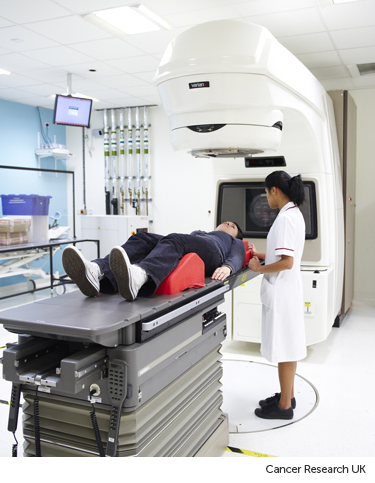
Before each treatment session
The radiographers help you to get onto the treatment couch. You might need to raise your arms over your head.
The radiographers line up the radiotherapy machine using the marks on your body. Once you are in the right position, they leave the room.
During the treatment
You need to lie very still. Your radiographers might take images (x-rays or scans) before your treatment to make sure that you're in the right position. The machine makes whirring and beeping sounds. You won’t feel anything when you have the treatment.
Your radiographers can see and hear you on a CCTV screen in the next room. They can talk to you over an intercom and might ask you to hold your breath or take shallow breaths at times. You can also talk to them through the intercom or raise your hand if you need to stop or if you're uncomfortable.
You won't be radioactive
This type of radiotherapy won't make you radioactive. It's safe to be around other people, including pregnant women and children.
Side effects
Radiotherapy for NHL can cause red, sore skin in the treatment area. And it can make you very tired. Other radiotherapy side effects vary, depending on the part of the body being treated. They include:
- diarrhoea
- feeling sick (nausea)
- hair loss in the treatment area
Side effects tend to start a few days after the radiotherapy begins. They gradually get worse during treatment. They can continue to get worse after your treatment ends. But they usually begin to improve 1 or 2 weeks after your treatment ends.
You might feel tired during your treatment. It tends to get worse as the treatment goes on. You might also feel weak and lack energy. Rest when you need to.
Tiredness can carry on for some weeks after the treatment has ended. But it usually improves gradually.
Various things can help you to reduce tiredness and cope with it, such as exercise. Some research has shown that taking gentle exercise can give you more energy. It's important to balance exercise with resting.
It is worth planning ahead if family commitments are going to make it difficult for you to rest. You will probably need more help as your treatment goes on.
If you are having radiotherapy to your brain as part of a stem cell transplant you might become very tired. Doctors call this somnolence syndrome. Some people are affected more than others. At it's worst, you could be asleep for most of the time for a while. But this does wear off.
The skin in the area being treated may become sore. On white skin the area may look red. On brown or black skin, the treatment area may darken slightly and have a different texture. It may take 4 to 6 weeks for this to get better.
Radiotherapy can inflame the lining of your bowel. This can cause diarrhoea. You may also have:
-
griping or cramping pain
-
an increase in wind
-
feeling you need to go to the toilet urgently
-
some mucus or blood in your poo (stool)
It’s important to drink plenty if you have diarrhoea, so you don't become dehydrated. Your doctor might prescribe tablets to help slow down your bowel if you need them. This should help to reduce the number of times you have diarrhoea. Changing your diet might also help lessen the number of times you need to go, such as reducing the amount of fibre if you have been following a diet very high in fibre. Ask your nurse or doctor about this.
Ask your nurse or radiographer for soothing creams to apply around your back passage (anus). The skin in that area can get very sore and might break if you have severe diarrhoea.
Diarrhoea should gradually get better a few weeks after your treatment has finished. Let your doctor or nurse know if it continues.
You might feel sick during the first few days after your radiotherapy treatment. Tell your doctor or nurse if you do feel sick. They can give you anti sickness medicine.
Radiotherapy can cause many different side effects, such as tiredness. The side effects you get will depend on the area you're having treatment to, but there are some general side effects you might experience regardless of where your cancer is. This video is about the general side effects you might have.
On screen text: Tiredness and weakness
Martin (Radiographer): As the normal cells repair themselves from the treatment this can use a lot of the body's resources, causing tiredness.
David: After about four weeks, I started to get tired. The body was starting to weaken.
Laurel: I was tired, day and night. Getting up in the morning was like a chore. I couldn't talk for 5 minutes. I would just sleep and just sleep and just wake up and sleep again.
Martin (Radiographer): Listen to your body. Take rests if you need to. Try not to overdo things.
Laurel: Don't fight with yourself too much. Just like go at a pace and just work with your body. If you can't make it today, you can't make it today.
David: You've got to rest. You have to take the time to rest.
Mary: Just going for them small walks. They really do help you. And even if it is just walking around your house or just walking around the block.
Martin (Radiographer): Doing exercise can help with tiredness by helping you maintain energy levels.
Mary: Being outside, that's a big, massive thing as well because you're feeling the fatigue and I think getting outside, just getting a bit of fresh air that really, really did help me.
Martin (Radiographer): The tiredness you can expect to begin within the first few weeks of treatment. Once it reaches its peak, about two weeks after treatment it recovers quite quickly after that.
Mary: It's not forever. You're not going to be like this forever and I did have to tell myself that.
Laurel: Two months after treatment, I start to feel less tired and that was a way forward because things start to really improve.
On screen text:
- Rest and have short naps when you need to
- Drink plenty of water
- Eat a balanced diet
- Do some gentle exercise
- Get some fresh air
On screen text: Sore skin
Martin (Radiographer): The radiotherapy can cause soreness of the skin. This only affects the area that you are having treated. This usually starts to appear about two weeks after you start treatment. You may notice this becoming more red and may become more itchy and sore as treatment continues.
David: After about ten days I started to get red on the area that they were targeting and it just progressively got redder and redder.
Laurel: My skin was dry and at the back was just like this triangle shape thing where it was like, okay, I'm a woman of colour, but it was really, really black.
David: Wasn't too painful, it was sort of annoying, rather than painful.
Martin (Radiographer): After treatment’s finished, the skin will remain sore for up to two weeks, but then recovers quite quickly.
Laurel: I haven’t got no scarring now at all.
David: It was maybe three or four weeks and then all the blemishes disappeared front and back.
Martin (Radiographer): When you start treatment we would advise you to carry on with your normal skincare routine but as the side effects develop, then your team will advise you on which products you can use on the skin safely.
Laurel: When I'm washing myself I use a sponge and you're just literally as it were just squirt it down, you don't rub the skin at all because it's already damaged. Pat dry, don't rub.
David: I spoke to the hospital about it and it was them that recommended this cream to put on, just to alleviate the symptoms.
Martin (Radiographer): We'd recommend wearing loose clothing and keeping the treatment area covered up against the sun and wind.
Laurel: I had to change most of my wardrobe. I only wore cotton.
David: Wearing T-shirts, soft clothing, nothing that would rub.
Mary: It's important when you go outside to make sure that you do wear that headscarf, or you do wear a hat or whatever it is.
Laurel: I wouldn't go in the sun at all, at all because my skin was - I know it was too delicate.
On screen text:
- Don’t rub the area, press if it is itchy and dab your skin dry
- Don’t use perfume, perfumed soaps or lotions on the area
- Don’t shave the area
- Only use creams or dressings advised by your specialist or radiographer
- Wear loose fitting clothing
- Avoid strong sun or cold winds
- Make sure you wear sunscreen
On screen text: Hair loss
Martin (Radiographer): Radiotherapy can cause hair loss in the area that's being treated, whereas chemotherapy can cause hair loss all over the body.
Mary: 2 to 3 weeks after the radiotherapy, I was brushing my hair and loads came out on the brush. I knew it was going to happen, but it was just hard when it happened.
Martin (Radiographer): In most cases the hair will grow back. This can take a couple of months and the hair may have a slightly different colour or texture.
Mary: Mine did grow back and there's a lot of grey in it so I have to dye it. This is not my original colour. It's very slow growing back.
Martin (Radiographer): Use a simple soap to clean the area. Be gentle with the skin in that area and after washing pat the area dry with a soft towel.
On screen text:
- Radiotherapy can make hair fall out in the treatment area
- It won’t cause hair to fall out in other parts of your body
- Your hair might grow back a few weeks after treatment ends
- If your hair won’t grow back, then your doctor should tell you
- Don’t use perfume, perfumed soaps, or lotions on the area
On screen text: Your mental health
Laurel: I felt frustrated. Some days were really, really challenging where there were just tears without words.
Mary: It's a mixture of emotions. You feel angry and you feel frustrated. You lose your confidence.
Martin (Radiographer): Radiotherapy can cause a lot of emotions at various times during the treatment. You may feel sad or anxious or depressed, which is quite normal. It's good to talk to people about your experiences, whether that's your team at the hospital or friends and family.
David: I couldn't praise the team highly enough. Everybody that was involved were unbelievable and if it hadn't been for them, I just don't think I would have gotten through with it.
Mary: I did have a nurse as well and she had the experience of dealing with people that went through brain surgery, went through radiotherapy so it was just great that I could reach out.
Martin (Radiographer): Your team will be able to give you information about local patient support services that are available, that includes things like counselling and complementary therapies.
Laurel: A referral from the hospital counselling, which I attended for about a year.
Martin (Radiographer): There's also lots of support available online and in your local area.
Mary: I went on loads of different forums and I spoke to loads of different people and it really, really helped me. If I didn't do that, I don't think I would have got through most days.
Laurel: If you get a bit cranky or feel a bit low, go for it. But there's so much help out there and that's why I'm pushing forward like don't sit down in silence. It's the same thing, just get the help you need.
On screen text:
- There is help available – ask the hospital for support
- Talk to your friends and family about how you are feeling
- Ask about local support groups
- Your GP or hospital can provide counselling
- You can get help and support online through forums
If you're experiencing a side effect that hasn't been covered in this video, you can find more information on the Cancer Research UK website.
On screen text: For more information go to: cruk.org/radiotherapy/side-effects
Travelling to radiotherapy appointments
You might have to travel a long way each day for your radiotherapy. This depends on where your nearest cancer centre is. This can make you very tired, especially if you have side effects from the treatment.
You can ask your radiographers for an appointment time to suit you. They will do their best, but some departments might be very busy. Some radiotherapy departments are open from 7 am till 9 pm.
Car parking can be difficult at hospitals. Ask the radiotherapy staff if you are able to get free parking or discounted parking. They may be able to give you tips on free places to park nearby.
Hospital transport may be available if you have no other way to get to the hospital. But it might not always be at convenient times. It is usually for people who struggle to use public transport or have any other illnesses or disabilities. You might need to arrange hospital transport yourself.
Some people are able to claim back a refund for healthcare travel costs. This is based on the type of appointment and whether you claim certain benefits. Ask the radiotherapy staff for more information about this and hospital transport.
Some hospitals have their own drivers and local charities might offer hospital transport. So do ask if any help is available in your area.



